
2025 EBA Stress Test: What You Need to Know
On July 5, 2024, the European Banking Authority (EBA) released the draft
rules for the 2025 EBA Stress Test, marking the beginning of the preparation
phase for banks. The supervisory authority will engage in workshops with bank
representatives to discuss the draft, with the final version anticipated by the
end of the year. Key developments and innovations can already be discerned
despite being in draft form.
Overview
As in previous years, the EBA’s stress test aims to assess the resilience of the European banking sector by subjecting large institutions in the EEA to a severe macroeconomic scenario. The impact of this scenario on the banks’ capital ratios will be calculated and publicly disclosed, influencing the 2025 Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP) and the setting of Pillar 2 Guidance (P2G). Banks will perform these calculations based on methodologies and scenarios provided by the EBA and ECB, subject to rigorous quality assurance.
Read below to find out how the entry into force of CRR3 with the shift of the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book (FRTB) affects credit and market risk, what role the additional requirements of market price risk and the centralization of net interest income (NII) play and what effects the additional proportionality has
Changes in Credit Risk
The application of CRR3 represents the most critical change in credit risk. Banks are now required to report figures for risk provisioning and RWA at both the starting point and in projections by CRR3. CRR3 directly impacts RWA calculations, especially with adjustments in risk weights within the Credit Risk Standardized Approach (CRSA). Notably, the newly introduced output floor adds operational complexity for internal ratings-based approach (IRB) institutions, requiring RWA simulations for IRB portfolios according to CRSA, which are recorded in a separate template. This output floor can materially affect earnings for IRB institutions in RWA simulations. Additionally, the non performing loans template has been expanded to include forbearance
information. The EBA has also set requirements for projecting risk provisioning at the economic sector level, particularly emphasizing the design of a loss distribution approach without sector-specific credit risk models.
Changes in market risk
In addition to the effects of CRR and FRTB, the requirements for market risk have been expanded overall. The full revaluation template now necessitates a breakdown by the issuer or borrower class and a more detailed breakdown of hedge relationships, replacing the previous long/short presentation. This aligns closely with the ad hoc data collection requirements on bond positions from 2023. Banks in the new, third proportionality class comprehensive approach (CA) advanced must also complete an additional section of the full revaluation template, showing the effect of six different scalings of the EBA stress scenario on options and their hedges in the trading portfolio. Moreover, the valuation reserves template now includes Funding Valuation Adjustments (FVAs) and sensitivities. Counterparty risk now considers the default of three counterparties instead of two, increasing the complexity of template completion for market risk.
Changes in Net Interest Income
Following the trend towards standardization, a central approach for NII projections will now be provided by the supervisory authority. While yet to be included in the published drafts, this approach will derive methodologically from intertemporal consistency formulas mandated since 2020. Banks can make their own projections only for derivatives margins. Additionally, funding matches for promotional loans will be reported and simulated separately to mitigate the one-sided impact of idiosyncratic shocks on liabilities. A longstanding criticism regarding including trading book positions in NII calculations, which led to implausible results in the 2023 stress test, has been addressed. Instruments with trading intent will largely be excluded from NII simulations, with recent average interest rate contributions extrapolated instead.
Changes in Operational Risk
CRR3 introduces substantial changes in operational risk. RWA must be reported as of the reporting date according to CRR2 and CRR3, with projections maintaining the CRR3 value. Banks applying the alternative standardized approach per CRR3 Article 314 (2a and 2b) must report transitional capital requirements. The new CRR3 business indicator approach must also be calculated at the starting point. Another key aspect is adjusting the multipliers for calculating projection floors, raising the floor for material behavioural risks and lowering it for non-material and other operational risks.
Proportionality Principle
The EBA has extended the proportionality principle to smaller banks with total assets under EUR 50 billion, previously reserved mainly for ECB-supervised banks outside the EBA group. Simplifications include reducing the number of country-currency pairs in reporting. Conversely, for banks with substantial market risk exposure (market risk RWA > 8% of total RWA), the EBA has introduced the Comprehensive Approach Advanced, which imposes stricter requirements.
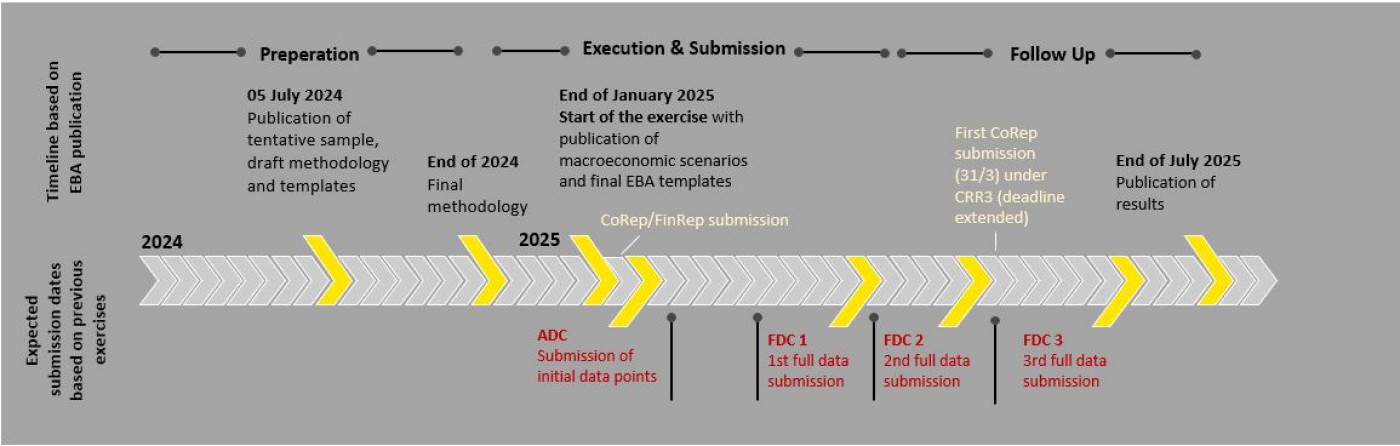
Procedure and Schedule
The EBA has announced that it will publish the final requirements at the end of 2024, with the stress test results to be released in July 2025. Consequently, the timetable is expected to mirror previous years. Particularly in the first quarter of 2025, there will be periods of heightened activity, with the submission of the initial data point in early March and the complete templates in early April. This timing coincides with the annual financial statements and the preparation of the first COREP report by CRR3. Banks should proactively prepare for this phase and allocate sufficient resources to manage these concurrent demands effectively.
For inquiries please contact:
regulatory-advisory@rbinternational.com
RBI Regulatory Advisory
Raiffeisen Bank International AG | Member of RBI Group | Am Stadtpark 9, 1030 Vienna, Austria | Tel: +43 1 71707 - 5923