
The GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) Standards
The GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) standards are a set of guidelines forming a framework for companies to report on their ESG (environment, social, and governance) performance consistently and comparably.
The GRI standards are currently voluntary and cover various topics, including climate change, human rights, labour practices, and anti-corruption. The standards help companies understand their impact on their environment by identifying, managing, and disclosing material ESG issues relevant to their business and stakeholders. Their origin dates back to 1997, in Boston, MA, USA, when the independent international organisation Global Reporting Initiative was formed. Since then, it relocated its base to Amsterdam, Netherlands, and its standards have evolved to become the most recognised global sustainability standards.
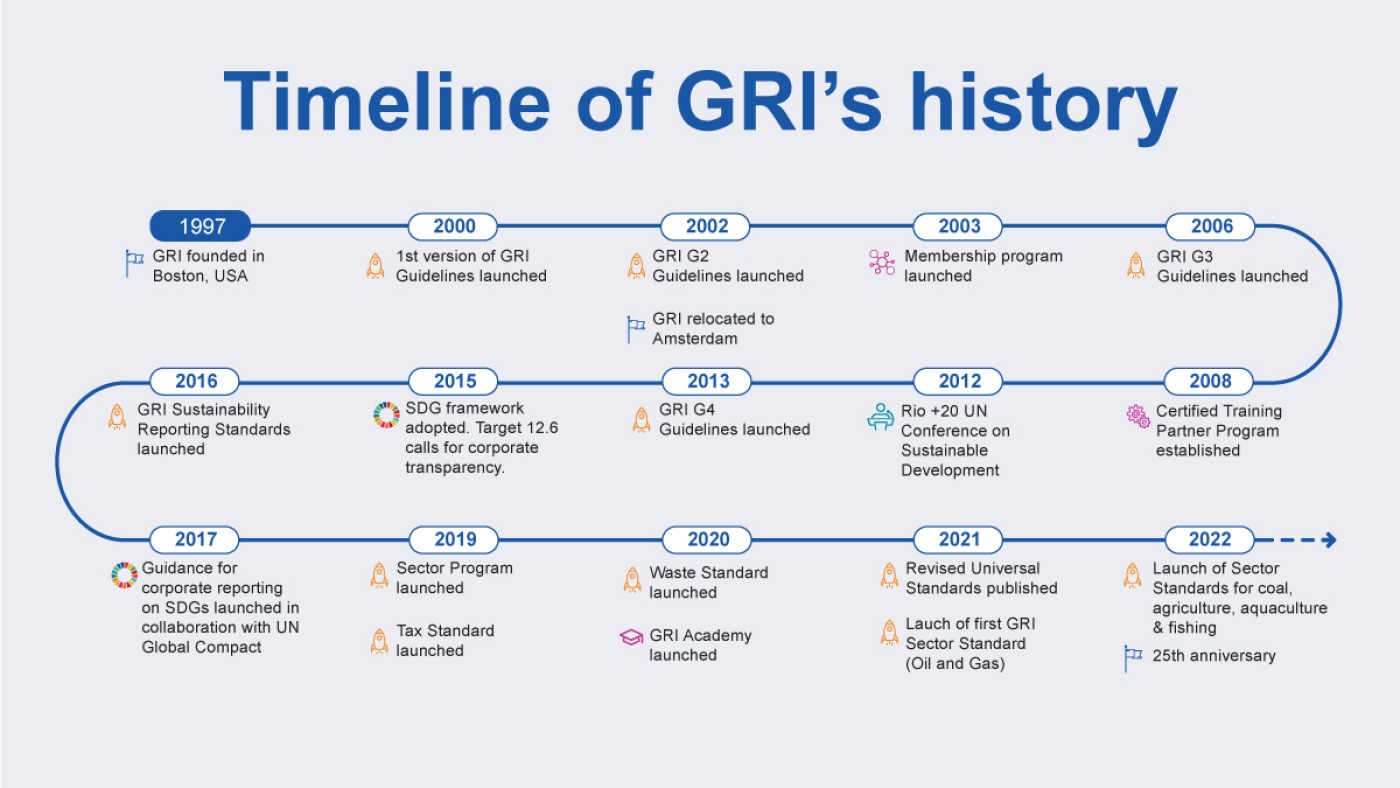
Source: https://www.globalreporting.org/about-gri/mission-history/
Today, the latest version of the GRI Standards was finalised on 30 June 2022 and is applicable as of 01 January 2023. It was issued by the Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB), an independently operating entity under the GRI. All institutions can align with these standards irrespective of their size, location, and sector. An institution can use the disclosed information to assess its strategies, policies, targets, goals, and KPIs. The respective stakeholders could then utilise these disclosures to evaluate the target institution. The credibility of the standards helps both parties make informed decisions.
The GRI standards are modular and cover:
- The GRI Universal Standards - set the rules for organizations to follow when reporting on their sustainability and environmental impact. These standards include GRI 1, which lays out the foundation and guidelines for reporting; GRI 2, which covers information about the organization's structure, governance, and engagement with stakeholders; and GRI 3, which details how an organization can identify and report on the topics that have the most significant impact on its operations and the steps the organization takes to manage them.
- The GRI Sector Standards - aim to enhance reporting quality, completeness, and consistency. These standards will be developed for 40 sectors starting with the highest impact, such as oil and gas, agriculture, aquaculture, and fishing. Each sector standard comprises an overview of the sector, a list of probable material topics, descriptions of the most significant impacts associated with the sector, and the necessary disclosures to report on these topics.
- The GRI Topic Standards - include a set of disclosures that provide information on various topics such as waste management, employee health and safety, and tax. Each standard consists of an overview of the topic and specific disclosures related to how the organization manages and addresses the associated impacts on the topic. An organization can choose the standards that align with the material topics they have identified and utilize them for reporting.
Currently, the GRI Standards are voluntary; however, various market participants are discussing a possible shift to mandatory. Nevertheless, once a company is GRI compliant, it is well prepared for the EU's European Sustainability Reporting Standards. The ESRS will be required in 2025 (for the financial year 2024) for companies already reporting under the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD); in 2026 (for FY 2025) for large companies covered by Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD); and in 2027 (for FY 2026) for listed SMEs, non-complex credit institutions and captive insurance undertakings. Given GRI's significant influence and involvement in drafting the ESRS, the requirements and disclosures will be of similar nature.
For inquiries please contact:
regulatory-advisory@rbinternational.com
RBI Regulatory Advisory
Raiffeisen Bank International AG | Member of RBI Group | Am Stadtpark 9, 1030 Vienna, Austria | Tel: +43 1 71707 - 5923